The global public cloud hosting market is projected to reach hundreds of billions of dollars by 2028, reflecting the increasing reliance on cloud services across various industries. However, organizations often grapple with cost optimization and security concerns. This growth highlights the importance of careful planning and management in public cloud hosting. This article serves as a comprehensive guide for IT managers, addressing key challenges while offering practical solutions to maximize the benefits of public cloud services.
Toc
- 1. Understanding Public Cloud Hosting Models
- 1.1. Service Models of Public Cloud Hosting
- 1.2. Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
- 1.3. Platform as a Service (PaaS)
- 1.4. Software as a Service (SaaS)
- 1.5. Emerging Models
- 1.6. Choosing the Right Public Cloud Provider
- 1.7. Key Factors to Consider
- 1.8. Leading Public Cloud Hosting Companies
- 1.9. Multi-Cloud and Hybrid Cloud Strategies
- 2. Optimizing Public Cloud Hosting Costs
- 3. Ensuring Security and Compliance in Public Cloud Hosting
- 4. Related articles 02:
- 5. Planning a Successful Cloud Migration
- 6. Leveraging Cloud Automation for Efficiency
- 7. Conclusion
- 8. Related articles 01:
Understanding Public Cloud Hosting Models
Public cloud hosting refers to a model where computing resources—such as servers, storage, and applications—are provided by third-party vendors over the internet. This setup allows multiple users to share these resources, enabling organizations to access cutting-edge technology without the substantial upfront investment associated with private cloud solutions.
Service Models of Public Cloud Hosting
Understanding the various service models available in public cloud hosting is essential for IT managers. The primary models include:
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
IaaS provides virtualized computing resources, allowing users to rent servers, storage, and networking capabilities as needed. This model offers significant flexibility and control, making it suitable for businesses that require customization.
Public Cloud Example: Amazon Web Services (AWS) stands out as a leading IaaS provider, offering a diverse range of services tailored to meet various business needs.
Platform as a Service (PaaS)
PaaS offers a platform for developers to build, deploy, and manage applications without needing to manage the underlying infrastructure. This model streamlines the development process by providing essential tools and libraries.
Public Cloud Example: Google Cloud Platform (GCP) provides PaaS solutions focused on application development and data analytics.
Software as a Service (SaaS)
SaaS delivers software applications via the internet, allowing users to access applications through web browsers without local installations. This model is popular among organizations seeking operational efficiency.
Public Cloud Example: Microsoft Office 365 exemplifies SaaS, providing productivity tools accessible from any internet-connected device.
Emerging Models
In addition to IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS, emerging models like Serverless and Function as a Service (FaaS) are gaining traction. These models enable developers to build applications without managing servers, further simplifying deployment and scaling.
Choosing the Right Public Cloud Provider
Selecting a suitable public cloud provider is a critical decision for IT managers. Various factors must be considered to ensure alignment with business goals.
Key Factors to Consider
- Cost: Analyze pricing models, including pay-per-use, reserved instances, and spot instances, to find the best fit for your organization.
- Security: Evaluate the security measures in place, including data encryption and access controls.
- Compliance: Ensure the provider adheres to relevant regulations, such as HIPAA and GDPR.
- Scalability: Assess the provider’s ability to scale resources according to your organization’s growth.
- Geographic Location: Consider data residency requirements and latency issues.
Leading Public Cloud Hosting Companies
Several public cloud hosting companies dominate the market, each with unique strengths and weaknesses:
- Amazon Web Services (AWS): Known for its extensive service offerings and global reach, AWS is a top choice for many enterprises.
- Microsoft Azure: Offers seamless integration with Microsoft products, making it ideal for organizations already utilizing Microsoft solutions.
- Google Cloud Platform (GCP): Focuses on data analytics and machine learning, appealing to businesses looking to leverage their data effectively.
- Alibaba Cloud: A significant player in Asia, providing a wide range of services tailored to regional businesses.
However, reliance on a single provider can lead to vendor lock-in, limiting flexibility and potentially increasing costs. Strategies such as employing a multi-cloud approach, utilizing different providers for distinct workloads, or adopting a hybrid cloud model that combines public and private resources can effectively mitigate this risk.
Multi-Cloud and Hybrid Cloud Strategies
IT managers should also consider multi-cloud and hybrid cloud strategies, which involve using multiple cloud providers or combining public and private cloud resources. These approaches can enhance flexibility and reduce the risk of vendor lock-in.
Optimizing Public Cloud Hosting Costs
While public cloud hosting offers substantial cost savings, effective cost management is essential to avoid overspending. Here, we will explore strategies for optimizing costs in public cloud environments.
Understanding Public Cloud Hosting Costs
Public cloud hosting costs can be categorized into several components:
- Compute Costs: Charges for virtual machines and processing power.
- Storage Costs: Fees associated with data storage solutions.
- Networking Costs: Expenses related to data transfer and bandwidth usage.
- Managed Services: Additional costs for services provided by the cloud vendor.
Pricing Models
Public cloud providers offer various pricing models, each with implications for budgeting:
- Pay-Per-Use: Charges based on actual resource consumption, suitable for fluctuating workloads.
- Reserved Instances: These offer significant discounts for committing to a fixed amount of capacity for a specific duration (1 or 3 years).
- Savings Plans: Introduced later, these offer similar discounts but provide more flexibility by allowing you to pay for actual usage within a defined commitment. For instance, a company consistently using 100 vCPUs might save 40-70% with a Reserved Instance compared to on-demand pricing.
- Spot Instances: Enables users to bid for unused capacity at lower rates, though availability can be unpredictable.
Public Cloud Hosting Free Options
Many cloud providers offer free tiers or trial periods, allowing organizations to explore their services without incurring costs. However, understanding the limitations of these free offerings is crucial to ensure they align with business needs.
While free tiers are attractive, they often come with significant limitations in terms of storage, compute power, and features. Moreover, exceeding these limits can quickly lead to unexpected charges, making careful planning crucial. Organizations should carefully evaluate their needs against the free tier’s limitations before committing.
Cost Optimization Techniques
To effectively control cloud spending, IT managers can implement several strategies:
- Right-Sizing Resources: Regularly assess resource utilization to ensure that instances are appropriately sized for workloads.
- Automation for Cost Management: Utilize automation tools to monitor and manage cloud resources, identifying and eliminating unused or underutilized resources.
- Cost Monitoring Tools: Implement cloud cost management tools to gain visibility into spending patterns and identify areas for optimization.
- Contract Negotiation: Engage in discussions with providers to negotiate terms and pricing based on expected usage.
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO)
Conducting a Total Cost of Ownership analysis can help organizations compare the costs of public cloud versus private cloud solutions. This analysis should consider all associated costs, including infrastructure, management, and operational expenses, to provide a comprehensive view of the financial implications.
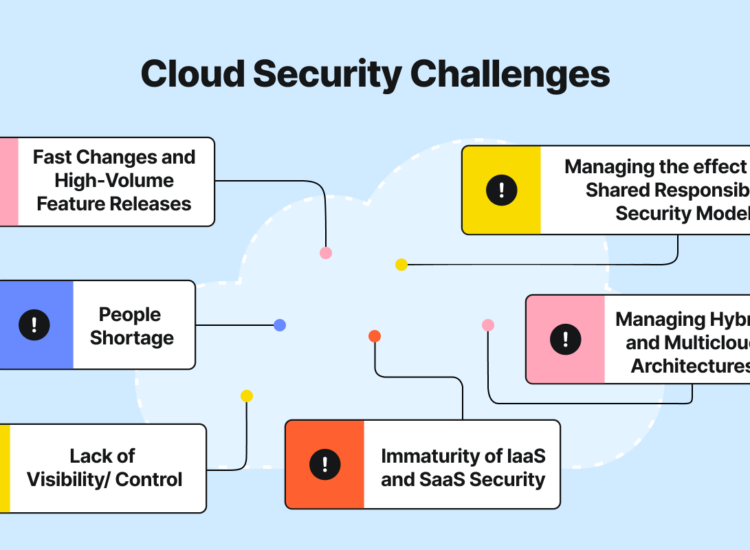
Ensuring Security and Compliance in Public Cloud Hosting
As organizations migrate to public cloud hosting, security and compliance become paramount concerns. Understanding the shared responsibility model and implementing security best practices is crucial for IT managers.
In the shared responsibility model, both the cloud provider and the organization share responsibilities for security. The provider is responsible for securing the underlying infrastructure, while the organization must protect its data and applications. This division of responsibility highlights the importance of collaboration between both parties.
Cloud Security Best Practices
To enhance security in public cloud environments, IT managers should consider the following best practices:
- Access Controls: Implement strong identity and access management policies to ensure that only authorized users have access to sensitive data.
- Data Encryption: Utilize encryption to protect data at rest and in transit, minimizing the risk of data breaches.
- Regular System Patching: Keep all systems and applications up to date with the latest security patches to mitigate vulnerabilities.
- Security Audits: Conduct regular security audits to identify and address potential weaknesses in the cloud environment.
Compliance Requirements
Organizations must also navigate various regulatory compliance requirements, such as HIPAA, GDPR, and PCI DSS. Understanding these regulations and ensuring compliance is essential for maintaining data security and avoiding legal issues.
Case Study: Successful Security Implementation
Consider a case study of a company that successfully addressed security challenges in their public cloud environment. By implementing robust access controls, encryption protocols, and regular security audits, the organization enhanced its overall security posture and maintained compliance with industry regulations.
1. https://bomnuocdailoan.com/mmoga-quickbooks-cloud-hosting-the-ultimate-guide-for-accounting-firms/
2. https://bomnuocdailoan.com/mmoga-find-the-best-managed-server-hosting-in-2024/
3. https://bomnuocdailoan.com/mmoga-cheap-cloud-hosting-the-ultimate-guide-for-small-businesses/
4. https://bomnuocdailoan.com/mmoga-the-best-video-hosting-platforms-for-educators-in-2024/
5. https://bomnuocdailoan.com/mmoga-the-ultimate-guide-to-best-magento-hosting-in-2024/
Planning a Successful Cloud Migration
Migrating to a public cloud environment requires careful planning and execution. IT managers must develop a comprehensive migration strategy to minimize disruptions and ensure a successful transition.
Step-by-Step Migration Process
- Assessment of Existing Infrastructure: Evaluate current workloads and determine which applications are suitable for migration to the public cloud.
- Selection of Migration Strategy: Choose a migration strategy that aligns with business goals, such as lift-and-shift, refactoring, or re-platforming.
- Data Migration Planning: Develop a detailed plan for data migration, including data transfer methods and timelines.
- Testing and Validation: Conduct thorough testing to ensure that applications function as expected in the new environment.
- Cutover: Execute the final cutover to the public cloud environment, minimizing downtime and disruptions to business operations.
Cloud Migration Tools
Various cloud migration tools are available to facilitate the migration process. These tools can assist with data transfer, application compatibility, and monitoring throughout the migration.
Minimizing Downtime During Migration
To minimize service disruptions during the migration process, IT managers should implement strategies such as phased migrations, real-time monitoring, and communication plans to keep stakeholders informed.
Post-Migration Optimization
After migration, ongoing monitoring and optimization are crucial for maintaining performance and managing costs. IT managers should establish a framework for regular reviews of resource utilization and cost management.
Leveraging Cloud Automation for Efficiency
Cloud automation plays a vital role in streamlining operations and reducing operational costs in public cloud environments. By automating routine tasks, organizations can improve efficiency and focus on strategic initiatives.
Defining Cloud Automation
Cloud automation refers to the use of tools and technologies to automate the deployment and management of cloud resources. This includes provisioning, scaling, and managing workloads without the need for manual intervention.
Cloud Automation Tools and Technologies
Several cloud automation tools are available to assist IT managers, including:
- Ansible: An open-source automation tool that allows users to define and manage their infrastructure as code.
- Chef: A configuration management tool that automates the deployment and management of applications.
- Puppet: A tool for automating infrastructure management, ensuring that systems are configured consistently and securely.
Benefits of Cloud Automation for IT Managers
Implementing cloud automation offers several benefits for IT managers:
- Reduced Manual Effort: Automating routine tasks frees up IT staff to focus on higher-level strategic initiatives.
- Improved Scalability: Automation enables organizations to scale resources quickly and efficiently in response to changing demands.
- Enhanced Security: Automated security controls can help identify and mitigate risks in real time.
- Faster Deployment Cycles: Automation streamlines the deployment process, enabling faster time to market for applications and services.
Current Trends in Cloud Automation
The rapid adoption of serverless computing, exemplified by AWS Lambda and Google Cloud Functions, is reshaping application development. By abstracting away server management, serverless drastically reduces operational overhead, improves scalability, and often leads to significant cost savings by only paying for actual compute time.
Practical Example of Cloud Automation
Consider an example of how cloud automation can streamline the deployment of a web application. By using Infrastructure as Code principles, IT teams can automate the provisioning of servers, configuration of networking, and deployment of application code. This not only speeds up the deployment process but also ensures consistency and reliability.
Conclusion
In summary, public cloud hosting presents a wealth of opportunities for organizations seeking to optimize their IT infrastructure. By understanding the various models, benefits, and strategies associated with public cloud hosting, IT managers can make informed decisions that align with their business objectives.
As organizations continue to navigate the complexities of cost management, security, and compliance in public cloud environments, it is essential to leverage the tools and strategies discussed in this guide. By doing so, IT managers can maximize the potential of public cloud hosting while effectively achieving their business goals.
1. https://bomnuocdailoan.com/mmoga-quickbooks-cloud-hosting-the-ultimate-guide-for-accounting-firms/
2. https://bomnuocdailoan.com/mmoga-the-ultimate-guide-to-best-magento-hosting-in-2024/
3. https://bomnuocdailoan.com/mmoga-the-best-video-hosting-platforms-for-educators-in-2024/
4. https://bomnuocdailoan.com/mmoga-cheap-cloud-hosting-the-ultimate-guide-for-small-businesses/
5. https://bomnuocdailoan.com/mmoga-find-the-best-managed-server-hosting-in-2024/